SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE MODELS (SDLC MODEL)
1) Waterfall Model
2) V-Shaped Model
3) Prototype Model
4) Spiral Model
5) Iterative Incremental Model
6) Big Bang Model
7) Agile Model
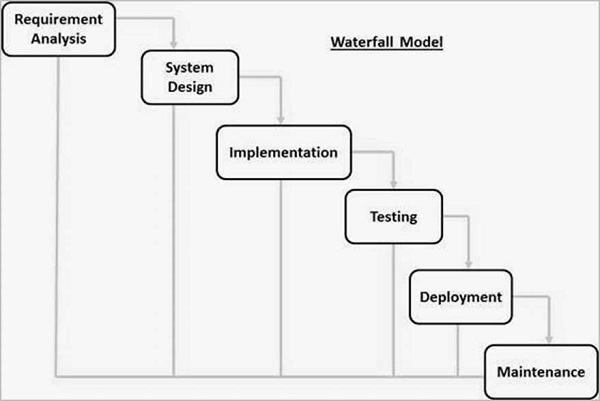
Waterfall Model
Sequential Phases in the Waterfall Model
- Requirement Analysis: The first phase involves understanding what needs to design and what is its function, purpose, etc. Here, the specifications of the input and output or the final product are studied and marked.
- System Design: The requirement specifications from the first phase are studied in this phase and system design is prepared. System Design helps in specifying hardware and system requirements and also helps in defining overall system architecture. The software code to be written in the next stage is created now.
- Implementation: With inputs from system design, the system is first developed in small programs called units, which are integrated into the next phase. Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality which is referred to as Unit Testing.
- Integration and Testing: All the units developed in the implementation phase are integrated into a system after testing of each unit. The software designed, needs to go through constant software testing to find out if there are any flaws or errors.
- Testing is done so that the client does not face any problem during the installation of the software.
- Deployment of System: Once the functional and non-functional testing is done, the product is deployed in the customer environment or released into the market.
- Maintenance: This step occurs after installation, and involves making modifications to the system or an individual component to alter attributes or improve performance. These modifications arise either due to change requests initiated by the customer, or defects uncovered during live use of the system. The client is provided with regular maintenance and support for the developed software.
Advantages of the Waterfall Model
- The advantage of waterfall development is that a schedule can be set with deadlines for each stage of development and a product can proceed through the development process model phases one by one.
- The waterfall model progresses through easily understandable and explainable phases and thus it is easy to use.
- It is easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model – each phase has specific deliverables and a review process.
- In this model, phases are processed and completed one at a time and they do not overlap. The waterfall model works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood.
Disadvantages of Waterfall Model
- It is difficult to estimate time and cost for each phase of the development process.
- Once an application is in the testing stage, it is very difficult to go back and change something that was not well-thought-out in the concept stage.
- Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects.
- Not suitable for the projects where requirements are at a moderate to high risk of changing.
V-Shaped Model
V-Model - Design
Under the V-Model, the corresponding testing phase of the development phase is planned in parallel. So, there are Verification phases on one side of the ‘V’ and Validation phases on the other side. The Coding Phase joins the two sides of the V-Model.
The following illustration depicts the different phases in a V-Model of the SDLC.
V-Model - Verification Phases
There are several Verification phases in the V-Model, each of these are explained in detail below.
Business Requirement Analysis
This is the first phase in the development cycle where the product requirements are understood from the customer’s perspective. This phase involves detailed communication with the customer to understand his expectations and exact requirement. This is a very important activity and needs to be managed well, as most of the customers are not sure about what exactly they need. The acceptance test design planning is done at this stage as business requirements can be used as an input for acceptance testing.
System Design
Once you have the clear and detailed product requirements, it is time to design the complete system. The system design will have the understanding and detailing the complete hardware and communication setup for the product under development. The system test plan is developed based on the system design. Doing this at an earlier stage leaves more time for the actual test execution later.
Architectural Design
Architectural specifications are understood and designed in this phase. Usually more than one technical approach is proposed and based on the technical and financial feasibility the final decision is taken. The system design is broken down further into modules taking up different functionality. This is also referred to as High Level Design (HLD).
The data transfer and communication between the internal modules and with the outside world (other systems) is clearly understood and defined in this stage. With this information, integration tests can be designed and documented during this stage.
Module Design
In this phase, the detailed internal design for all the system modules is specified, referred to as Low Level Design (LLD). It is important that the design is compatible with the other modules in the system architecture and the other external systems. The unit tests are an essential part of any development process and helps eliminate the maximum faults and errors at a very early stage. These unit tests can be designed at this stage based on the internal module designs.
Coding Phase
The actual coding of the system modules designed in the design phase is taken up in the Coding phase. The best suitable programming language is decided based on the system and architectural requirements.
The coding is performed based on the coding guidelines and standards. The code goes through numerous code reviews and is optimized for best performance before the final build is checked into the repository.
Validation Phases
The different Validation Phases in a V-Model are explained in detail below.
Unit Testing
Unit tests designed in the module design phase are executed on the code during this validation phase. Unit testing is the testing at code level and helps eliminate bugs at an early stage, though all defects cannot be uncovered by unit testing.
Integration Testing
Integration testing is associated with the architectural design phase. Integration tests are performed to test the coexistence and communication of the internal modules within the system.
System Testing
System testing is directly associated with the system design phase. System tests check the entire system functionality and the communication of the system under development with external systems. Most of the software and hardware compatibility issues can be uncovered during this system test execution.
Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing is associated with the business requirement analysis phase and involves testing the product in user environment. Acceptance tests uncover the compatibility issues with the other systems available in the user environment. It also discovers the non-functional issues such as load and performance defects in the actual user environment.
V- Model ─ Application
V- Model application is almost the same as the waterfall model, as both the models are of sequential type. Requirements have to be very clear before the project starts, because it is usually expensive to go back and make changes. This model is used in the medical development field, as it is strictly a disciplined domain.
The following pointers are some of the most suitable scenarios to use the V-Model application.
Requirements are well defined, clearly documented and fixed.
Product definition is stable.
Technology is not dynamic and is well understood by the project team.
There are no ambiguous or undefined requirements.
The project is short.
Advantages of V Model−
This is a highly-disciplined model and Phases are completed one at a time.
Works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood.
Simple and easy to understand and use.
Easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model. Each phase has specific deliverables and a review process.
Disadvantages of V Model −
High risk and uncertainty.
Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects.
Poor model for long and ongoing projects.
Not suitable for the projects where requirements are at a moderate to high risk of changing.
Once an application is in the testing stage, it is difficult to go back and change a functionality.
No working software is produced until late during the life cycle.
Prototype Model
- Rapid Throwaway Prototyping –
This technique offers a useful method of exploring ideas and getting customer feedback for each of them. In this method, a developed prototype need not necessarily be a part of the ultimately accepted prototype. Customer feedback helps in preventing unnecessary design faults and hence, the final prototype developed is of a better quality. - Evolutionary Prototyping –
In this method, the prototype developed initially is incrementally refined on the basis of customer feedback till it finally gets accepted. In comparison to Rapid Throwaway Prototyping, it offers a better approach which saves time as well as effort. This is because developing a prototype from scratch for every iteration of the process can sometimes be very frustrating for the developers.
Advantages –
- The customers get to see the partial product early in the life cycle. This ensures a greater level of customer satisfaction and comfort.
- New requirements can be easily accommodated as there is scope for refinement.
- Missing functionalities can be easily figured out.
- Errors can be detected much earlier thereby saving a lot of effort and cost, besides enhancing the quality of the software.
- The developed prototype can be reused by the developer for more complicated projects in the future.
- Flexibility in design.
Disadvantages –
- Costly w.r.t time as well as money.
- There may be too much variation in requirements each time the prototype is evaluated by the customer.
- Poor Documentation due to continuously changing customer requirements.
- It is very difficult for the developers to accommodate all the changes demanded by the customer.
- There is uncertainty in determining the number of iterations that would be required before the prototype is finally accepted by the customer.
- After seeing an early prototype, the customers sometimes demand the actual product to be delivered soon.
- Developers in a hurry to build prototypes may end up with sub-optimal solutions.
- The customer might lose interest in the product if he/she is not satisfied with the initial prototype.
Spiral Model
Spiral model is one of the most important Software Development Life Cycle models, which provides support for Risk Handling. In its diagrammatic representation, it looks like a spiral with many loops. The exact number of loops of the spiral is unknown and can vary from project to project. Each loop of the spiral is called a Phase of the software development process. The exact number of phases needed to develop the product can be varied by the project manager depending upon the project risks. As the project manager dynamically determines the number of phases, so the project manager has an important role to develop a product using spiral model.
The Radius of the spiral at any point represents the expenses(cost) of the project so far, and the angular dimension represents the progress made so far in the current phase.
- Objectives determination and identify alternative solutions(Planning): Requirements are gathered from the customers and the objectives are identified, elaborated and analyzed at the start of every phase. Then alternative solutions possible for the phase are proposed in this quadrant.
- Identify and resolve Risks(Risk Analysis): During the second quadrant all the possible solutions are evaluated to select the best possible solution. Then the risks associated with that solution is identified and the risks are resolved using the best possible strategy. At the end of this quadrant, Prototype is built for the best possible solution.
- Develop next version of the Product(Design): During the third quadrant, the identified features are developed and verified through testing. At the end of the third quadrant, the next version of the software is available.
- Review and plan for the next Phase(Evaluation): In the fourth quadrant, the Customers evaluate the so far developed version of the software. In the end, planning for the next phase is started.
The Spiral model is called as a Meta Model because it subsumes all the other SDLC models. For example, a single loop spiral actually represents the Iterative Waterfall Model. The spiral model incorporates the stepwise approach of the Classical Waterfall Model. The spiral model uses the approach of Prototyping Model by building a prototype at the start of each phase as a risk handling technique. Also, the spiral model can be considered as supporting the evolutionary model – the iterations along the spiral can be considered as evolutionary levels through which the complete system is built.
Advantages of Spiral Model: Below are some of the advantages of the Spiral Model.
- Risk Handling: The projects with many unknown risks that occur as the development proceeds, in that case, Spiral Model is the best development model to follow due to the risk analysis and risk handling at every phase.
- Good for large projects: It is recommended to use the Spiral Model in large and complex projects.
- Flexibility in Requirements: Change requests in the Requirements at later phase can be incorporated accurately by using this model.
- Customer Satisfaction: Customer can see the development of the product at the early phase of the software development and thus, they habituated with the system by using it before completion of the total product.
Disdvantages of Spiral Model: Below are some of the main disadvantages of the spiral model.
- Complex: The Spiral Model is much more complex than other SDLC models.
- Expensive: Spiral Model is not suitable for small projects as it is expensive.
- Too much dependable on Risk Analysis: The successful completion of the project is very much dependent on Risk Analysis. Without very highly experienced expertise, it is going to be a failure to develop a project using this model.
- Difficulty in time management: As the number of phases is unknown at the start of the project, so time estimation is very difficult.





Comments
Post a Comment